Whether an ischemic stroke is due to a noncardiogenic or cardiogenic source, the mechanism of causing a stroke is the same. Both sources are involved with the development of thrombi or emboli that move from their original source to the brain blocking blood flow in the process. Thrombosis (from Ancient Greek θρόμβωσις thrómbōsis clotting”) is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injure the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss. Even when a blood vessel is not injure blood clots.
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain in cell death. There are two main types of stroke : ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both result in parts of the brain not functioning properly. Signs and symptoms of a stroke may include an inability to move or feel on one side of the body, problems understanding or speaking.
About Thromboembolic Stroke Prophylaxis: Measures taken to prevent a Thromboembolic Stroke , the formation of a blood clot (thrombus) inside one of the blood vessels, stopping blood flow to a part of the brain. ThromboembolisFormation in a blood vessel of a clot (thrombus) that breaks loose and is carried by the blood stream to plug another vessel. Thromboembolism is a significant cause of morbidity (disease) and mortality (death), especially in adults. The prevalence increases rapidly with age, to 2. Patients with cancer who develop ischemic strokes often have metastatic disease and may be at high risk for other thromboembolic events.
Their cause of stroke frequently differs from the general population and is commonly attributed to unconventional mechanisms related to hypercoagulability, such as nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis. A thrombotic stroke is a type of ischemic stroke that occurs when a blood clot, also called a thrombus, blood clot forms and blocks blood flow through the artery in which it formed. The blood clot may block the flow of oxygen-rich blood to a portion of the brain, causing long-term brain damage.
This type of brain damage caused by a lack of adequate blood supply produces a stroke. Several models of thromboembolic stroke have been developed in a variety of animal species. Nevertheless, the use of transgenic animals to further investigate mechanisms that control neuronal, glial, or endothelial outcome after stroke, including inflammatory processes, blood–brain barrier leakage or disruption, and neurotoxicity, requires. This causes brain cells in that area to stop functioning and die quickly. The clot blocks blood flow to a part of the brain.
The blood clot that triggers a thrombotic stroke usually forms inside an artery that already has been narrowed by atherosclerosis. The risk is greatest right after a stroke and decreases over time. The likelihood of severe disability and death increases with each recurrent stroke.
About of people who have had a stroke have a second stroke within days of their first stroke , and about one-third have a second stroke within years. Focused Ultrasound Foundation. Background and Purpose—After cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis (CVT), there is an increased risk of further venous thromboembolic events (VTEs). Time to a second cerebral or systemic venous thrombotic event and risk factors for recurrence have not been investigated in large prospective studies. If artery-to-artery embolism is suspecte see management algorithm in Large Vessel section.
Consider induced hypertension to determine if symptoms can be ameliorated with augmented CBF. Ralph Sacco, MD: Good afternoon and welcome to this special symposium titled Keeping an Eye on Thromboembolic Stroke. My name is Ralph Sacco and I am chairman of neurology at the University of Miami, Miller School of Medicine, Jackson Memorial Hospital in Florida. Prevention of stroke and systemic thromboembolism remains the cornerstone for management of atrial fibrillation (AF) and flutter. Multiple risk assessment models for stroke and systemic thromboembolism are currently available.
The score, with its known limitations, remains as the recommended risk stratification tool in most major guidelines. A novel mouse model of thromboembolic stroke. Illustration of the mouse model of thromboembolic stroke.

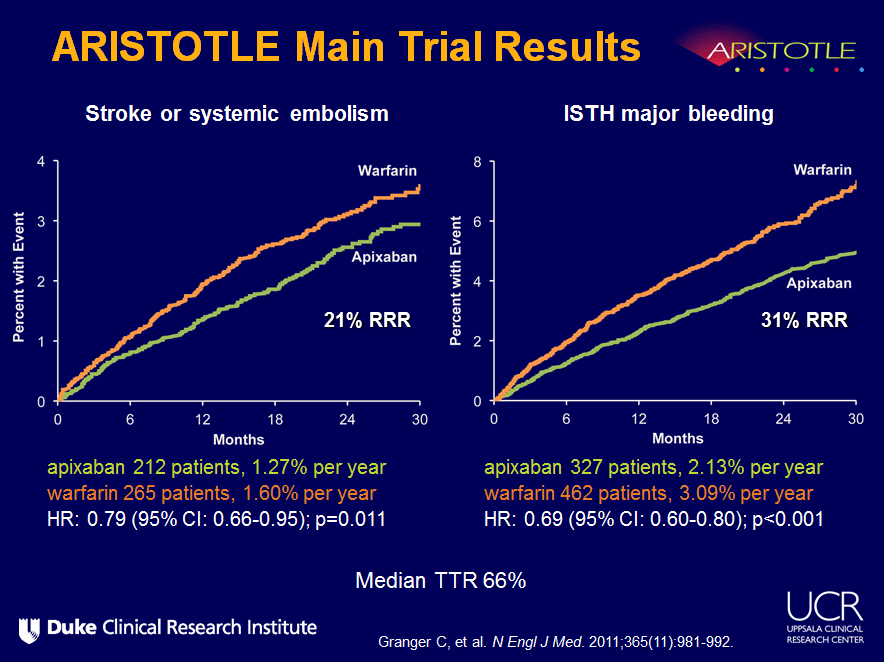
A) The Circle of Willis and major cerebral vessels visualized on the mouse brain ventral surface after intravenous ink dye injection. ABSTRACTGregory PC, Kuhlemeier KV: Prevalence of venous thromboembolism in acute hemorrhagic and thromboembolic stroke. Hazard ratios ( confidence intervals) for thromboembolic stroke , intracranial hemorrhage, major extracranial bleeding, and all-cause mortality from sensitivity analyses in elderly patients treated with warfarin, dabigatran, rivaroxaban, or apixaban for nonvalvular atrial fibrillation.
Hiç yorum yok:
Yorum Gönder
Not: Yalnızca bu blogun üyesi yorum gönderebilir.