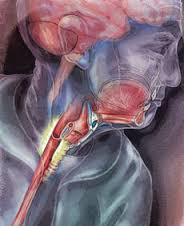
Your stroke may cause a swallowing disorder called dysphagia. If not identified and manage it can lead to poor nutrition, pneumonia and disability. Aspiration is a common problem for people with dysphagia. It occurs when something you’ve swallowed enters the airway and lungs. The presence of dysphagia has been associated with an increased risk for pulmonary complications and even mortality.

There is emerging evidence that early detection of dysphagia in patients with. How common is dysphagia after stroke ? Numerous studies have tried to establish the incidence of dysphagia after stroke with figures ranging from to. At first glance, these figures seem to represent a wide range.
The explanation for this lies in variations in study design and in the identification of dysphagia , both of which merit further discussion. Objective— To determine the incidence of dysphagia and associated pulmonary compromise in stroke patients through a systematic review of the published literature. Causes of oropharyngeal dysphagia include: Neurological disorders. Sudden neurological damage, such as from a stroke or brain or spinal cord injury, can affect your ability to swallow.
Although it improves within weeks for most, some face longstanding swallowing problems that place them at risk for pneumonia, malnutrition, dehydration, and significantly affect quality of life. Dysphagia affects the vast majority of acute stroke patients. Food or drink might go down the wrong way and get into your lungs.
This is called dysphagia. Your speech pathologist can help you manage dysphagia. Evaluating swallowing and nutrition after stroke. Literature reports a wide range of incidence of dysphagia after a stroke, but the reader must look at.
For people with dysphagia , eating becomes a challenge. The consequences may be serious. Someone who cannot swallow safely is at high risk of choking, pulmonary aspiration and may not be able to.
A person can have dysphagia without odynophagia (dysfunction without pain), odynophagia without dysphagia (pain without dysfunction) or both together. Work closely with your medical team for support. If you inhale food or liquid on accident, it can bring bacteria into the lungs and lead to aspiration pneumonia. It takes your brain, several nerves and muscles, two muscular valves, and an open, unconstricted esophagus, or swallowing tube to. Post- stroke dysphagia (a difficulty in swallowing after a stroke ) is a common and expensive complication of acute stroke and is associated with increased mortality, morbidity, and institutionalization due in part to aspiration, pneumonia, and malnutrition.
Almost half of people who have a stroke will have some difficulties in the first few weeks. Swallowing problems ( dysphagia ) are very common after a stroke. Learn about the causes and treatment of swallowing problems. Some causes of dysphagia are explained here. Damage to the nervous system (in the brain and spinal cord) can interfere with the nerves responsible for starting and controlling swallowing.
A stroke is distressing for both the patient and their family. It is caused by a disruption of the blood supply to a part of the brain, either by a blood clot (most common) or a weakened blood vessel. Common conditions after stroke – dysphagia and central facial paralysis.
Because all our bodily functions are controlled by the brain, the symptoms will vary depending on where in the brain the stroke occurred and the degree and scope of the damage. However, with the right knowledge, mindset, support system, and stroke recovery expertise, a survivor’s dysphagia has every likelihood of improving. IT can happen after a stroke , depending on what part of the brain is affected.
Weak tongue or cheek muscles may make it hard to move food around in the mouth for chewing. A stroke or other nervous system disorder may make it difficult to start the swallowing response, a stimulus that allows. It can result in a range of problems including those related to movement and balance, memory loss or thinking problems, loss or blurring of vision, depression, and swallowing difficulties known as dysphagia , which can lead to malnutrition.
A stroke can be distressing for both the patient and their loved ones. When a person has trouble swallowing, he or she may have problems moving food or liquid from the mouth to the stomach, called dysphagia. Stroke is a common cause of dysphagia. About one-third of these people will need treatment for pneumonia at some point.
About of people with dysphagia have aspiration. What causes aspiration from dysphagia ?
Hiç yorum yok:
Yorum Gönder
Not: Yalnızca bu blogun üyesi yorum gönderebilir.