The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of thickness: for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. The following is engineering properties of water. Dynamic viscosity of water. The dynamic viscosity of water is 8. Water is a chemical compound with the chemical formula H2O.
A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms that are connected by covalent bonds. A Newtonian fluid is defined as the shear stress equal to the absolute viscosity multiplied by the rate of shearing strain (change in speed over the change in height). Body temperature (o C) is another commonly used viscosity measure. Water has a low viscosity due to the low inter-molecular bonds.
In the metric system, the unit of kinematic viscosity is the square centimeter per second or the stoke. Water Density as a function of Temperature and Salinity. In this video we will learn the complete procedure for finding out the absolute viscosity of bitumen.
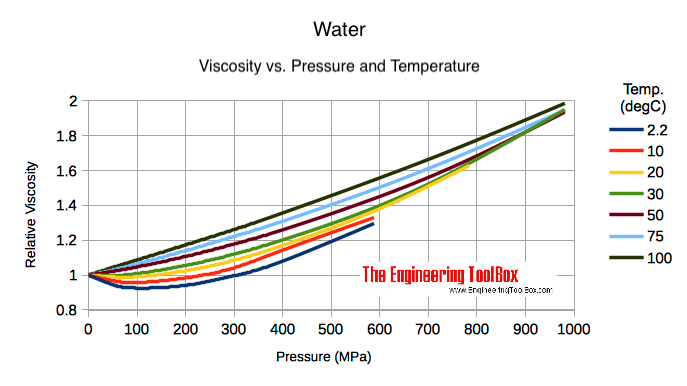
Water at a temperature of 20°C has a Relative density of 0. The more common unit is centipoise (cP). This online unit converter allows quick and accurate conversion between many units of measure, from one system to another. In this paper an attempt has been made to find temperature dependent dynamic (or absolute ) viscosity of some common domestic usable Oil namely Soya bean Oil, Coconut oil, Kerosene oil and 2T Oil.
The Poise is used in the table because of its more common usage. Define absolute viscosity. English dictionary definition of absolute viscosity. In liquids it usually decreases with temperature, whereas in gases it increases.
This article discusses several models of this dependence, ranging from rigorous first-principles calculations for monatomic gases, to empirical correlations for liquids. Understanding the temperature dependence of viscosity is important in many applications, for instance. It is the ratio of the dynamic viscosity to its density, a force independent quantity.
Viscosity depends strongly on temperature. The absolute viscosity of oil gives a number of the oil’s exact film thickness. Kinematic viscosity can be obtained by dividing the absolute viscosity of a fluid.

Such a value is important for testing oil in the field or in manufacturing facilities. At degrees Celsius, the dynamic, or absolute , viscosity of water is 1. The kinematic viscosity of water is 1. For example, water has less resistance to flow than syrup or molasses and therefore has a lower viscosity. Of all the test employed for used oil analysis, none provides better test repeatability or consistency than viscosity.
It decreases with increase in temperature. In practical terms, it is closely related to how thick the substance is. Both absolute and kinematic viscosity change according to temperature.
The higher the viscosity , the longer it takes to flow through the tube (i.e. a fluid with less viscosity will take less time to flow than a fluid with higher viscosity ). The calculator on this site is for informative purposes only and we make no claims as to the accuracy, completeness or fitness for any particular purpose of the produced by our calculators. Godfrey An accurate knowledge of the viscosities of liquids in absolute units is of fundamental importance in many scientific fields. The measurement of these viscosities is almost universally based upon the absolute viscosity of water at 20° C as a primary standard.
In the case of non-Newtonian fluids, the ratio varies with. The two most common types of viscosity are dynamic and kinematic. Absolute viscosity is also known as.

The relationship between these two properties is quite straightforward.
Hiç yorum yok:
Yorum Gönder
Not: Yalnızca bu blogun üyesi yorum gönderebilir.