Ciliary body is a tissue in the eye which consists of ciliary muscles and processes. The ciliary muscles are used to set the focus of the eye lens either by stretching or contracting the lens. Introduction Flight is very visually demanding but other behaviors important as well! Start studying Chapter 17.

Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Adjustment of the lens by the ciliary body : a. Reveal the answer to this question whenever you are ready. Enter another question to find a notecard: Search. About the flashcard: This flashcard is meant to be used for studying, quizzing and learning new information. Many scouting web questions are common questions that are.
The lens is part of the anterior segment of the human eye. In front of the lens is the iris, which regulates the amount of light entering into the eye. Posterior to the lens is the vitreous body , which, along.
Get your by asking now. Contains muscles that control the shape of the lens and secrete. We see discounts on products. Normally, the accommodative process, or accommodation, of the crystalline lens is smooth and effortless.
When one changes one’s focus from far to near, the ciliary muscle quickly contracts, causing the crystalline lens to accommodate (become thicker) and the object at a near distance to become clear. The ciliary fibers have circular (Ivanoff), longitudinal and radial orientations. When the ciliary muscle contracts.
Function : The main function of the ciliary body is the accomodation of the eyes to light. Close vision : In order to focus on near objects within about meters the eye must make the following adjustments. Constriction of the pupils Pupil.
The ciliary body changes the size and shape of the lens by contracting and relaxing. What is the combining form for “hearing”? This refractory adjustment to focus as an object draws near is accommodation.
Muscles of the ciliary body produce flattening of the lens for distance vision and thickening and rounding of the lens for close vision. The iris and pupil also play important roles in making sight possible. You can switch focus from looking at your hand to a distant object in less than one-tenth of a second. This bends the light rays inwards more sharply. How do eyes adjust to different distances?
Muscles in the ciliary body enable the flexible lens to alter its shape and allow the eye to focus on objects. The present invention relates to accommodative intraocular lens (AIOL) assembly comprising a lens in the human eye ciliary sulcus self-anchoring implant, for AIOL along a human eye is required to maintain the visual axis of the eye position fixing system and the implant (AMI) in an animal comprising adjusting the experimental ocular. Produced by a structure alongside the lens called the ciliary body , the aqueous passes first into the posterior chamber (between the lens and iris) and then flows forward through the pupil into the anterior chamber of the eye. This adjustment of the lens is known as accommodation (see also below). The vitreous humor is produced in the non-pigmented portion of the ciliary body.
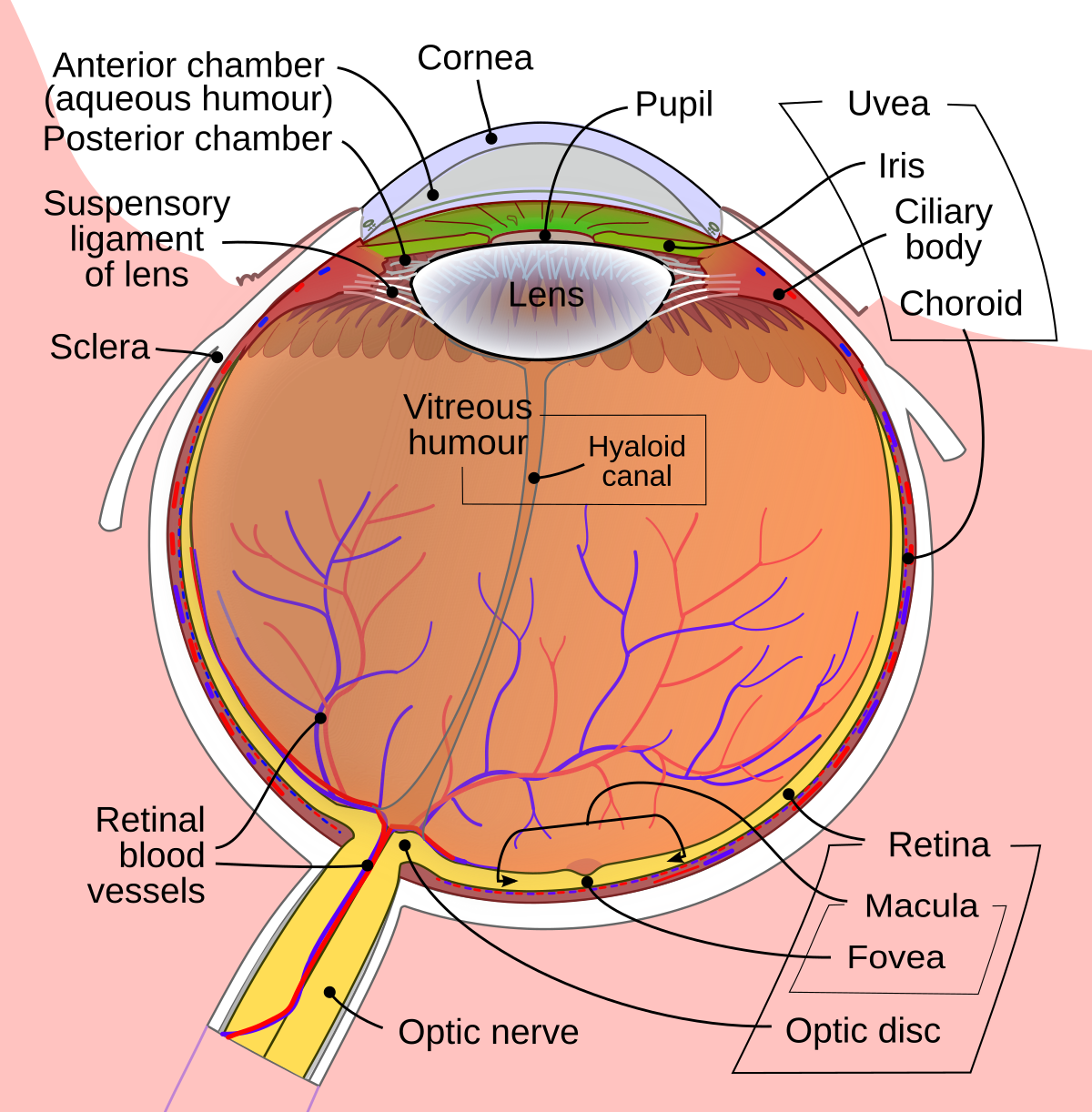
The invention relates to an accommodative lens implant, controlled by the ciliary muscle and consisting of at least one or more lenses (1 17), which are preferably made of a biocompatible material and lie on a common optical axis. According to the invention, the lens or lenses form part of a flexible, sealed implant body that is transparent in the vicinity of the actual lens. Home Anatomy of the Eye. Choroid: Layer of the eye behind the retina,.
SURGICAL INTERVENTION AND ACCOMMODATIVE RESPONSES: I. CENTRIPETAL CILIARY BODY , CAPSULE AND LENS MOVEMENT IN RHESUS MONKEYS OF VARYING AGE. For the younger animals, this meant an adjustment to the presbyopic condition at an earlier age. Surgically altering the. The ocular projections of the autonomic nervous system influence numerous functions of the eye.
These include: 1) pupil diameter and ocular accommodation, which are controlled by the intrinsic muscles of the eye located in the iris and ciliary body respectively – these structures are innervated by postganglionic fibers from the ciliary (parasympathetic) and superior cervical.
Hiç yorum yok:
Yorum Gönder
Not: Yalnızca bu blogun üyesi yorum gönderebilir.